Aplicação da tecnologia pinch por meio de programa computacional para o planejamento de uma rede de trocadores de calor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47456/bjpe.v8i4.38062Palavras-chave:
Redes de Vapor, Simulink, Matlab, Balanço Energético, SimulaçãoResumo
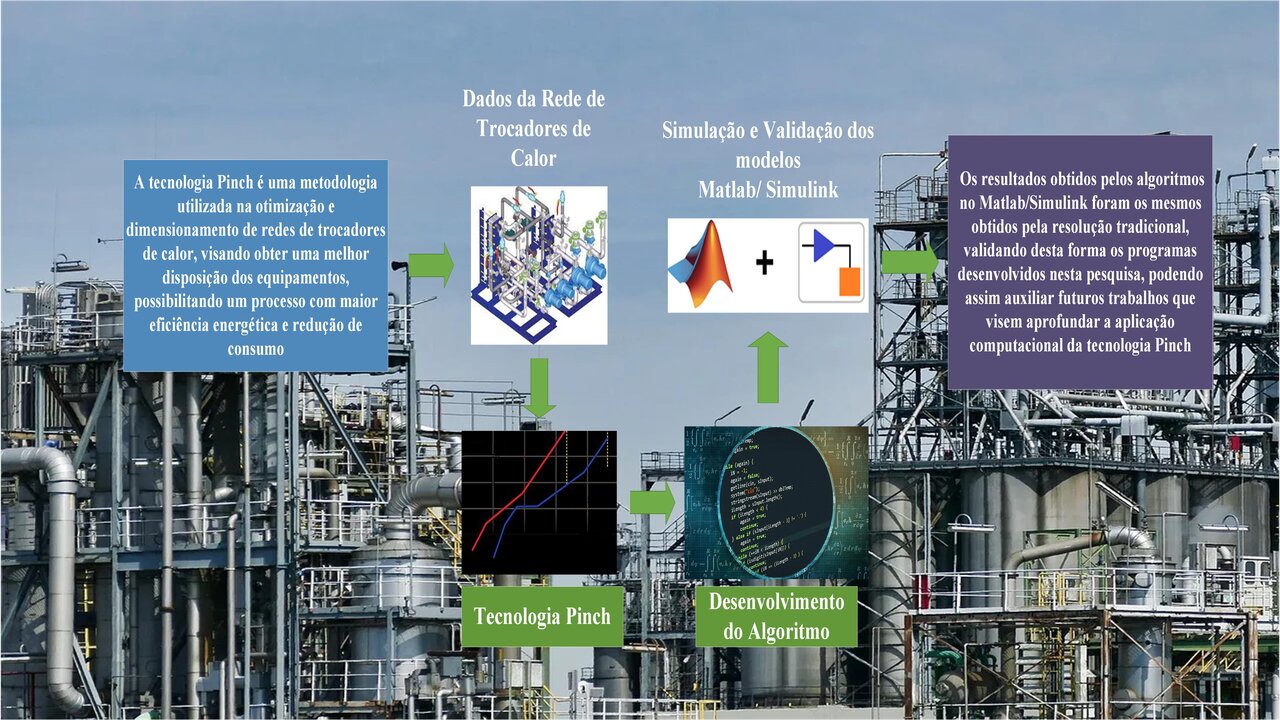
A tecnologia Pinch é uma metodologia utilizada na otimização e dimensionamento de redes de trocadores de calor, desenvolvida inicialmente por Hohnmann e Linnhoff durante a crise do petróleo em meados dos anos 70 e 80. A tecnologia Pinch visa obter melhor disposição dos equipamentos, possibilitando um processo com maior eficiência energética e redução de consumo. Neste trabalho foi desenvolvido um algoritmo computacional por meio da ferramenta Matlab e sua extensão para simulação de processos, o Simulink, para aplicar os princípios da tecnologia Pinch na resolução computacional de uma situação problema envolvendo uma rede de trocadores de calor. Inicialmente, foi selecionada uma situação problema envolvendo tecnologia Pinch, que foi resolvida de maneira tradicional. A partir disso o algoritmo computacional foi desenvolvido no Matlab, baseando-se nos princípios da tecnologia Pinch e fazendo uso dos dados pertencentes ao problema selecionado para estudo; realizando uma comparação dos dados originais e os encontrados pelo algoritmo para assim validar o programa desenvolvido. Após a validação do algoritmo, foi utilizado o Simulink para o desenvolvimento de um programa em linguagem de blocos, a fim de se proporcionar uma melhor visualização gráfica dos resultados obtidos, comparando-os mais uma vez com os resultados da resolução tradicional. Os resultados obtidos pelos algoritmos no Matlab/Simulink foram os mesmos obtidos pela resolução tradicional, validando desta forma os programas desenvolvidos nesta pesquisa, podendo assim auxiliar futuros trabalhos que visem aprofundar a aplicação computacional da tecnologia Pinch.
Downloads
Referências
Arrotéia, D. R. (2019). Aplicação da metodologia Pinch em uma planta de tratamento de gordura. Centro Universitário FEI. https://repositorio.fei.edu.br/bitstream/FEI/3039/1/fulltext.pdf
Deveque, R. (2019). Aplicação da metodologia Pinch de integração energética em um processo de síntese da amônia. Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso. Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná. http://repositorio.roca.utfpr.edu.br/jspui/handle/1/12502
Guimarães, E. E. X. F. (2019). Otimização energética não paramétrica de uma planta de biodiesel via tecnologia Pinch. Universidade Federal do Maranhão (UFMA). https://rosario.ufma.br/jspui/handle/123456789/4330
Hohmann, E. C. J. (1971). Optimun network for heat exchange. PhD Dissertation – University of Sounthern California, Los Angeles, CA https://www.proquest.com/openview/9df67d6f157aba5c0e6f68106665f34b/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
Jalalvand, A. R., Roushani, M., Goicoechea, H. C., Rutledge, D. N., & Gu, H. W. (2019). MATLAB in electrochemistry: A review. Talanta, 194, 205-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.041 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.041
Linnhoff, B. (1983). User guide on process integration for the efficient use of energy. AIChE J., v. 28. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10003395547/
Marques, J. A. (2018). Integração de Processo Utilizando a Tecnologia PINCH. Universidade Católica de Pernambuco. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1H4L2JXhvbZ_vxrak8CVgWb1JHrc3yAKC/view
Módenes, A. N. (1995). Síntese de redes de trocadores de calor flexíveis. Dissertação de Mestrado. Universidade Estadual de Maringá. http://repositorio.uem.br:8080/jspui/bitstream/1/3828/1/000079904.pdf
Olsen, D., Abdelouadoud, Y., Liem, P., & Wellig, B. (2017). The role of Pinch analysis for industrial ORC integration. Energy Procedia, 129, 74-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.09.193 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.09.193
Palú, F. (1995). Otimização da distribuição de área em redes de trocadores de calor. Dissertação de Mestrado. Universidade Estadual de Maringá. http://repositorio.uem.br:8080/jspui/handle/1/3792
Roque, M. C. (2000). Desenvolvimento de software para a sintese de rede de trocadores de calor considerando projeto detalhado e a flexibilidade do sistema. Universidade Estadual de Campinas. https://1library.org/document/zw0kp8vy-desenvolvimento-software-trocadores-considerando-projeto-detalhado-flexibilidade-sistema.html
Tomita, T., Ishii, D., Murakami, T., Takeuchi, S., & Aoki, T. (2019). A scalable Monte-Carlo test-case generation tool for large and complex simulink models. In: 2019 IEEE/ACM 11th International Workshop on Modelling in Software Engineering (MiSE). IEEE, p. 39-46. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8876967 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MiSE.2019.00014
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2022 Brazilian Journal of Production Engineering

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Atribuição 4.0 internacional CC BY 4.0 Deed
Esta licença permite que outros remixem, adaptem e desenvolvam seu trabalho não comercialmente, contanto que eles creditem a você e licenciem suas novas criações sob os mesmos termos.