Epidemiological profile of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in the city of Vitória - Espírito Santo
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47456/bjpe.v9i1.39945Keywords:
Lupus, Epidemiology, Comorbidities, DATASUSAbstract
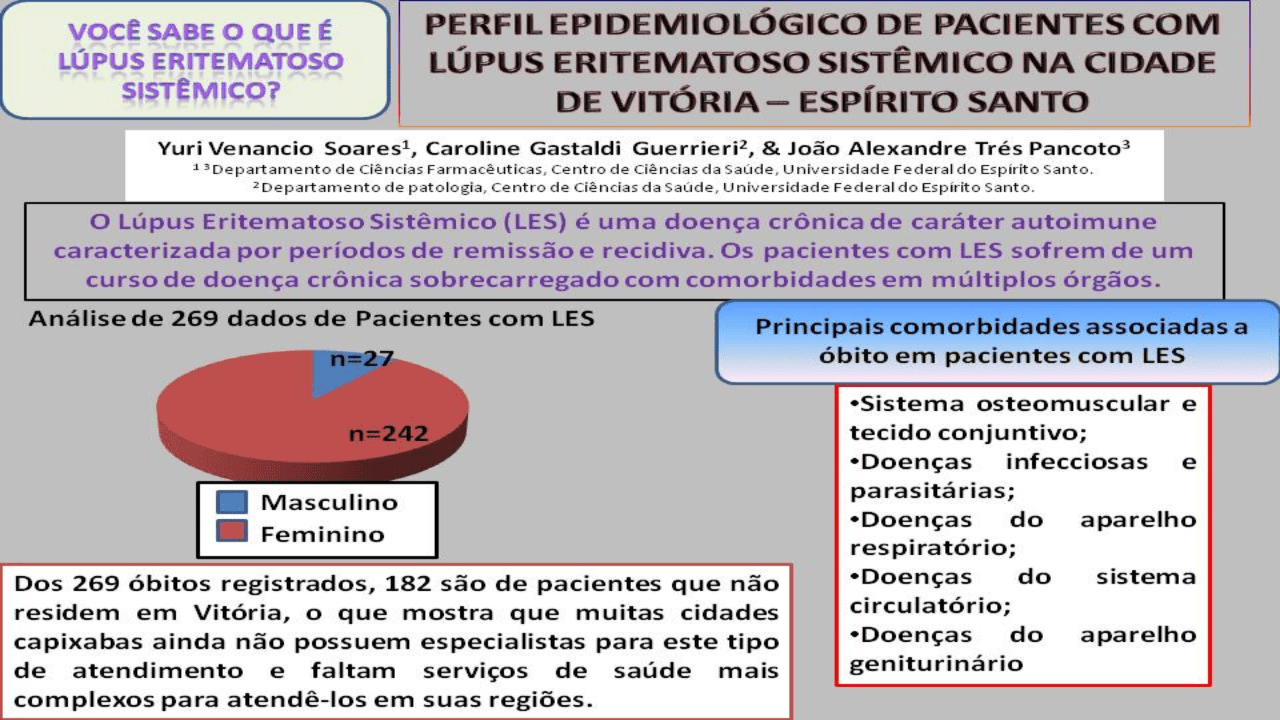
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by periods of remission and relapse. Patients with SLE suffer from a chronic disease course burdened with multi-organ comorbidities. Epidemiological studies on SLE are very scarce in Brazil, mainly in the state of Espírito Santo. In view of this scarcity of epidemiological data, the present study carried out an epidemiological research in patients with SLE, characterizing the causes of mortality in the municipality of Vitória between 2009 and 2019, using the DATASUS database. According to the analysis of deaths of patients with SLE that occurred in Vitória (n=269), the main underlying causes of death were diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, infectious and parasitic diseases, diseases of the respiratory system, diseases of the circulatory system and diseases of the genitourinary system, which together represented 84.39% of death records. The female sex had a higher number of deaths compared to men, the results were significant for women of brown and white ethnicity, aged between 10-49 years, in addition, this age group had the highest number of deaths in Vitória. Of the 269 deaths recorded, 182 are of patients who do not live in Vitória, which shows that many cities in Espírito Santo still do not have specialists for this type of care and there is a lack of more complex health services to assist them in cities in the interior of Espírito Santo.
Downloads
References
Abdou, N. I., Wall, H., Lindsley, H. B., Halsey, J. F., & Suzuki, T. (1981). Network theory in autoimmunity. In vitro suppression of serum anti-DNA antibody binding to DNA by anti-idiotypic antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of clinical investigation, 67(5), 1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci110158 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI110158
Amaral, B., Murphy, G., Ioannou, Y., & Isenberg, D. A. (2014). A comparison of the outcome of adolescent and adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 53(6), 1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket488 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket488
Andrade, R. M., & Alarcón, G. S. (2006). Antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: benefits beyond disease activity. Future Rheumatol, 1(2), p. 225–233. 10.2217/17460816.1.2.225 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2217/17460816.1.2.225
Assis, M. R. D., & Baaklini, C. E. (2009). Lúpus eritematoso sistêmico. RBM rev. bras. med, 274-285.
Bruce, I. N., O'Keeffe, A. G., Farewell, V., Hanly, J. G., Manzi, S., Su, L., Gladman, D. D., Bae, S. C., Sanchez-Guerrero, J., Romero-Diaz, J., Gordon, C., Wallace, D. J., Clarke, A. E., Bernatsky, S., Ginzler, E. M., Isenberg, D. A., Rahman, A., Merrill, J. T., Alarcón, G. S., Fessler, B. J., … Urowitz, M. B. (2015). Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) Inception Cohort. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 74(9), 1706–1713. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205171 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205171
Camelier, Aquiles. (2005). O Pulmão e as Doenças Reumáticas. Recuperado em 19 de janeiro, 2022 de: https://www.reumatologia.org.br/orientacoes-ao-paciente/o-pulmao-e-as-doencas-reumaticas/
Chakravarty, E. F., Bush, T. M., Manzi, S., Clarke, A. E., & Ward, M. M. (2007). Prevalence of adult systemic lupus erythematosus in California and Pennsylvania in 2000: estimates obtained using hospitalization data. Arthritis and rheumatism, 56(6), 2092–2094. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22641 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22641
Choi, J., Kim, S. T., & Craft, J. (2012). The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus-an update. Current opinion in immunology, 24(6), 651–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2012.10.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2012.10.004
Costi, L. R., Iwamoto, H. M., Neves, D. C. de O., & Caldas, C. A. M. (2017). Mortalidade por lúpus eritematoso sistêmico no Brasil: avaliação das causas de acordo com o banco de dados de saúde do governo. REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE REUMATOLOGIA, 57(6) 574–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbre.2017.09.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbr.2017.05.007
Danza, A., & Ruiz-Irastorza, G. (2013). Infection risk in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: susceptibility factors and preventive strategies. Lupus, 22(12), 1286–1294. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203313493032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203313493032
Datta, S. K., & Kalled, S. L. (1997). CD40-CD40 ligand interaction in autoimmune disease. Arthritis and rheumatism, 40(10), 1735–1745. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780401002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780401002
Fan, Y., Hao, Y. J., & Zhang, Z. L. (2020). Systemic lupus erythematosus: year in review 2019. Chinese medical journal, 133(18), 2189–2196. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000983 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000983
Fava, A., & Petri, M. (2019). Systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis and clinical management. Journal of autoimmunity, 96, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.11.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.11.001
Gergianaki, I., Garantziotis, P., Adamichou, C., Saridakis, I., Spyrou, G., Sidiropoulos, P., & Bertsias, G. (2021). High comorbidity burden in patients with SLE: data from the community-based lupus registry of crete. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050998 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050998
Hahn, B. H., McMahon, M. A., Wilkinson, A., Wallace, W. D., Daikh, D. I., Fitzgerald, J. D., Karpouzas, G. A., Merrill, J. T., Wallace, D. J., Yazdany, J., Ramsey-Goldman, R., Singh, K., Khalighi, M., Choi, S. I., Gogia, M., Kafaja, S., Kamgar, M., Lau, C., Martin, W. J., Parikh, S., … American College of Rheumatology (2012). American College of Rheumatology guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis care & research, 64(6), 797–808. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21664 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21664
Hsu, C. Y., Chiu, W. C., Yang, T. S., Chen, C. J., Chen, Y. C., Lai, H. M., Yu, S. F., Su, Y. J., & Cheng, T. T. (2011). Age- and gender-related long-term renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus, 20(11), 1135–1141. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203311404912 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203311404912
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). (2021). Projeção da população do Brasil e das Unidades da Federação. Recuperado em 06 de setembro, 2021 de: https://www.ibge.gov.br/apps/populacao/projecao/index.html
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). (2016). International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)-WHO Version for ;2016. Recuperado em 01 de janeiro, 2022 em: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2016/en
Ishitani, Lenice Harumi, & França, Elisabeth. (2001). Uso das causas múltiplas de morte em saúde pública. Informe Epidemiológico do Sus, 10(4), 163-175. https://dx.doi.org/10.5123/S0104-16732001000400003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5123/S0104-16732001000400003
Julian, G. S., Rosim, R. P., Carneseca, E. C., & Rigolon, J. (2020). Annualized hospitalization rate with natalizumab vs fingolimod in second-line treatment for RRMS in the public healthcare system in Brazil: A claim database approach. PloS one, 15(3), e0229768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229768 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229768
Justiz Vaillant, A. A., Goyal, A., Bansal, P., & Varacallo, M. (2021). Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Kernder, A., Richter, J. G., Fischer-Betz, R., Winkler-Rohlfing, B., Brinks, R., Aringer, M., Schneider, M., & Chehab, G. (2021). Delayed diagnosis adversely affects outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus: Cross sectional analysis of the LuLa cohort. Lupus, 30(3), 431–438. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320983445 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320983445
Klumb, E. M., Scheinberg, M., Souza, V. A., Xavier, R. M., Azevedo, V. F., McElwee, E., Restrepo, M. R., & Monticielo, O. A. (2021). The landscape of systemic lupus erythematosus in Brazil: An expert panel review and recommendations. Lupus, 30(10), 1684–1695. https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033211030008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033211030008
Krishnan, E., & Hubert, H. B. (2006). Ethnicity and mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in the US. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 65(11), 1500–1505. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.040907 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.040907
Lee, S. J., Silverman, E., & Bargman, J. M. (2011). The role of antimalarial agents in the treatment of SLE and lupus nephritis. Nature reviews. Nephrology, 7(12), 718–729. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2011.150 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2011.150
McGill, G., & Ambrose, N. (2018). The management of lupus in young people. The British journal of general practice: the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners, 68(667), 96–97. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp18X694805 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp18X694805
McGlasson, S., Wiseman, S., Wardlaw, J., Dhaun, N., & Hunt, D. (2018). Neurological Disease in Lupus: Toward a Personalized Medicine Approach. Frontiers in immunology, 9, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01146 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01146
Mendoza, J. (2021). Number of licensed rheumatologists in Brazil between 2013 and 2018. Recuperado em 05 de janeiro, 2022 de: https://www.statista.com/statistics/962380/number-licensed-rheumatologists-brazil/
Mok, C. C. (2005). Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Lupus, 14(1), 39–44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203305lu2057oa
Moulton, V. R., Suarez-Fueyo, A., Meidan, E., Li, H., Mizui, M., & Tsokos, G. C. (2017). Pathogenesis of Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cellular Perspective. Trends in molecular medicine, 23(7), 615–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2017.05.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2017.05.006
Murimi-Worstell, I. B., Lin, D. H., Nab, H., Kan, H. J., Onasanya, O., Tierce, J. C., Wang, X., Desta, B., Alexander, G. C., & Hammond, E. R. (2020). Association between organ damage and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ open, 10(5), e031850. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031850 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031850
Nakashima, C. A., Kenji. G., Ana Paula., Silva, J. F. M. da., Fiorenzano, G. Rodrigues., Santos, A. B. da Silva dos., Leite, M. F. Silva., Nogueira, M. Augusto., Menolli, P. V. da Silva., & Menolli, R. Andrade. (2011). Incidência e aspectos clínico-laboratoriais do Lúpus eritematoso sistêmico em cidade do Sul do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Reumatologia, 51(3), 235–239. 10.1590/s0482-50042011000300004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0482-50042011000300004
Niewold, T. B., Hua, J., Lehman, T. J., Harley, J. B., & Crow, M. K. (2007). High serum IFN-alpha activity is a heritable risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes and immunity, 8(6), 492–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364408 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364408
Pego-Reigosa, J. M., Nicholson, L., Pooley, N., Langham, S., Embleton, N., Marjenberg, Z., Barut, V., Desta, B., Wang, X., Langham, J., & Hammond, E. R. (2021). The risk of infections in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 60(1), 60–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa478 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa478
Pestka, S., Krause, C. D., & Walter, M. R. (2004). Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunological reviews, 202, 8–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00204.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00204.x
Petri M. (2002). Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology, 16(5), 847–858. https://doi.org/10.1053/berh.2002.0259 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/berh.2002.0259
Ramírez Sepúlveda, J. I., Bolin, K., Mofors, J., Leonard, D., Svenungsson, E., Jönsen, A., Bengtsson, C., DISSECT consortium, Nordmark, G., Rantapää Dahlqvist, S., Bengtsson, A. A., Rönnblom, L., Sjöwall, C., Gunnarsson, I., & Wahren-Herlenius, M. (2019). Sex differences in clinical presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Biology of sex differences, 10(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-019-0274-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-019-0274-2
Rider, V., Jones, S., Evans, M., Bassiri, H., Afsar, Z., & Abdou, N. I. (2001). Estrogen increases CD40 ligand expression in T cells from women with systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of rheumatology, 28(12), 2644–2649. Recuperado de: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11764210/
Roved, J., Westerdahl, H., & Hasselquist, D. (2017). Sex differences in immune responses: Hormonal effects, antagonistic selection, and evolutionary consequences. Hormones and behavior, 88, 95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.11.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.11.017
Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Danza, A., & Khamashta, M. (2012). Glucocorticoid use and abuse in SLE. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 51(7), 1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker410 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker410
Sagawa, Akira., & Abdou, Nabih. (1978). Suppressor-Cell Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus CELLS INVOLVED AND IN VITRO CORRECTION. The Journal of clinical investigation, 62(4), 789–796. 0021-9738/78/1001-789 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI109190
Schwartzman-Morris, J., & Putterman, C. (2012). Gender differences in the pathogenesis and outcome of lupus and of lupus nephritis. Clinical & developmental immunology, 2012, 604892. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/604892 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/604892
Skare, T. L., Dagostini, J. S., Zanardi, P. I., & Nisihara, R. M. (2016). Infections and systemic lupus erythematosus. Einstein (Sao Paulo, Brazil), 14(1), 47–51. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-45082016AO3490 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-45082016AO3490
Sociedade Brasileira de Reumatologia. (2019). Lúpus Eritematoso Sistêmico (LES). Recuperado em 25 de agosto, 2021 em: https://www.reumatologia.org.br/doencas/principais-doencas/lupus-eritematoso-sistemico-les/
Souza, D. C., Santo, A. H., & Sato, E. I. (2010). Trends in systemic lupus erythematosus mortality rates in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil from 1985 to 2004. Clinical and experimental rheumatology, 28(4), 519–524.
Tedde-Filho, G., Nunes, M. S., Júnior, J. C. G., Júnior, W. D., Peterle, V. U., & Gomides, A. P. M. (2021). Hospital admissions and mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Development, 7(6), 54091–54100. 10.34117/bjdv7n6-011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv7n6-011
Voss, A., Laustrup, H., Hjelmborg, J., & Junker, P. (2013). Survival in systemic lupus erythematosus, 1995–2010. A prospective study in a Danish community. Lupus, 22(11), 1185-1191. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203313498796 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203313498796
Weckerle, C. E., & Niewold, T. B. (2011). The unexplained female predominance of systemic lupus erythematosus: clues from genetic and cytokine studies. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology, 40(1), 42–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8192-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8192-4
World Health Organization. (2016). International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)-WHO Version for, 2016. Recuperado em 01 de setembro, 2021 em: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2016/en
Yap, D. Y., & Lai, K. N. (2015). Pathogenesis of renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus--the role of autoantibodies and lymphocytes subset abnormalities. International journal of molecular sciences, 16(4), 7917–7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047917 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047917
Zeller, C. B., & Appenzeller, S. (2008). Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of traditional and lupus related risk factors. Current cardiology reviews, 4(2), 116–122. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340308784245775 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/157340308784245775
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Brazilian Journal of Production Engineering

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.