Systematic literature review: towards an industry 4.0 maturity model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47456/bjpe.v9i5.42677Keywords:
Maturity Model, Industry 4.0, Review of the Literature, TEMACAbstract
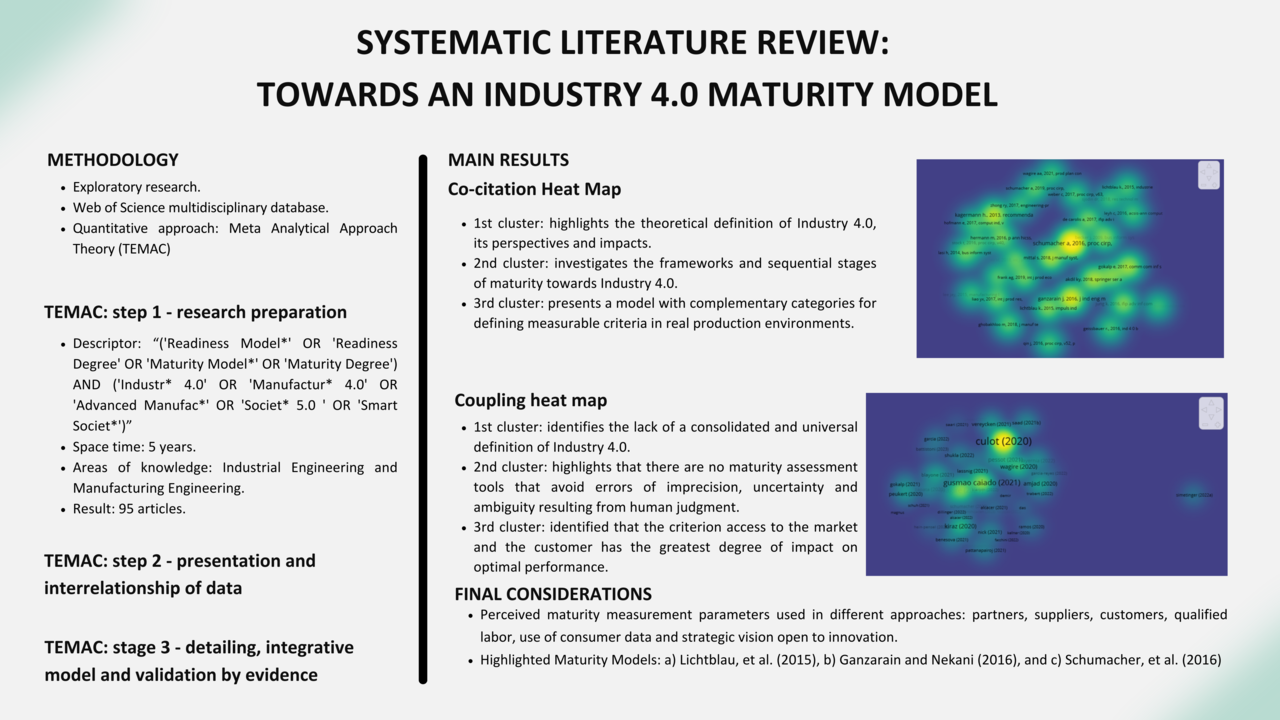
Nowadays, compared to the 4th Industrial Revolution, the industry needs to be competitive, innovative and incorporate digital technologies. This challenge and quest for competitiveness needs support in view of the escalation of potential maturity levels that a company can reach, which makes it essential to measure business maturity. maturity in Industry 4.0. using the Consolidated Meta-Analytic Approach Theory (TEMAC) to identify impact literature and bibliometric analyses. Based on the analysis of several articles found, criteria were identified for a maturity model for industry 4.0, namely: assistance from partners, suppliers and customers, as well as qualified labor, use of consumer data and strategic vision open to innovation. The concern with SMEs in this literature was evident, which are more numerous and prone to launch themselves in industry 4.0. This research also revealed the opportunity to develop a specific maturity model capable of meeting the recent demand for a theoretical and practical framework that helps measure the maturity of companies in Industry 4.0.
Downloads
References
Brennen, J. S. & Kreiss, D. (2016). Digitalization. The International Encyclopedia of Communication Theory and Philosophy. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118766804.wbiect111 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118766804.wbiect111
Caiado, R. G. G., Scavarda, L. F., Gavião, L. O., Ivson, P., Nascimento, D. L., & Reyes, J. A. G. (2021). A fuzzy rule-based industry 4.0 maturity model for operations and supply chain management. International Journal of Production Economics, 231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107883 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107883
Confederação Nacional da Indústria - CNI (2016). Desafios para a indústria 4.0 no Brasil. Distrito Federal: Brasília. Recuperado de https://static.portaldaindustria.com.br/media/filer_public/d6/cb/d6cbfbba-4d7e-43a0-9784-86365061a366/desafios_para_industria_40_no_brasil.pdf
Confederação Nacional da Indústria - CNI (2018). Indústria e digitalização da economia. Distrito Federal: Brasília. Recuperado de http://www.portaldaindustria.com.br/cni/canais/propostas-da-industria-para-eleicoes-2018/downloads/
Culot, G., Nassimbeni, G., Orzes, G., & Sartor, M. (2020). Behind the definition of Industry 4.0: Analysis and open questions. International Journal of Production Economics, 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107617 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107617
Fontanela, C., dos Santos Araújo Silva dos Santos, M. I., & da Silva Albino, J. (2020). A sociedade 5.0 como instrumento de promoção dos direitos sociais no Brasil. Revista Justiça Do Direito, 34(1), 29-56. https://doi.org/10.5335/rjd.v34i1.10904 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5335/rjd.v34i1.10904
Ganzarain, J. & Nekane, E. (2016). Three stage maturity model in SME's toward industry 4.0. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management - JIEM, 9(5), 1119-1128. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.2073 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.2073
Gil, A. C. (2023). Como elaborar projetos de pesquisa. Atlas, 7. São Paulo.
Hofmann, E., & Rusch, M. (2017). Industry 4.0 and the current status as well as future prospects on logistics. Computers in Industry, 89, 23-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.002
Kagermann, H., Wahlster, W., & Helbig, J. (2013). Recommendations for implementing the strategic initiative Industrie 4.0. Recuperado de https://www.din.de/resource/blob/76902/e8cac883f42bf28536e7e8165993f1fd/recommendations-for-implementing-industry-4-0-data.pdf
Kiraz, A., Canpolat, O., Ozkurt, C., & Taskin, H. (2020). Analysis of the factors affecting the Industry 4.0 tendency with the structural equation model and an application. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106911
Kohlegger, M., Maier, R., & Thalmann, S. (2009). Understanding maturity models results of a structured content analysis. Proceedings of I-KNOW ’09 and I-SEMANTICS ’09, 51-61. Recuperado de https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=d4bbb80e3abd240a3a617a6f27fcd68d87e65f99
Kosacka-Olejnik, M. & Werner-Lewandowska, K. (2018). How mature is reverse logistics? Concept of the process and resource oriented maturity model. ACTA Technica Napocensis, 61(4). Recuperado de https://atna-mam.utcluj.ro/index.php/Acta/article/view/1099/1025
Lavoie, D. & Culbert, A. (1978). Stages in organization development. Journal of Interior Design, 31(5). https://doi.org/10.1177/001872677803100503 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/001872677803100503
Lichtblau, K., Guericke, D., & Stich, V. (2015). IMPULS - Industrie 4.0 - Readiness. Recuperado de https://www.industrie40-readiness.de/
Mariano, A. M. & Rocha, M. S. (2017). Revisão da Literatura: Apresentação de uma Abordagem Integradora. AEDEM International Conference. Recuperado de https://www.pesquisatemac.com/_files/ugd/344d4e_63c8f403712b44beacb0e45f3a5a07ec.pdf
Mittal, S., Khan, M. A., Romero, D., & Wuest, T. (2018). A critical review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity models: Implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 49, 194-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.10.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.10.005
Oztemel, E. & Gursev, S. (2020). Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31, 127-182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1433-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1433-8
Pereira, A. C. & Romero, F. (2017). A review of the meanings and the implications of the Industry 4.0 concept. Procedia Manufacturing, 13, 1206-1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.032
Schumacher, A., Erol, S., & Sihn, W. (2016). A Maturity Model for Assessing Industry 4.0 Readiness and Maturity of Manufacturing Enterprises. Procedia CIRP, 52, 161-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.07.040 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.07.040
Schwab, K. (2019). A quarta revolução industrial. Edipro. São Paulo.
Silva, I. A., & Barbalho, S. C. M. (2019). Modelos de maturidade do CMM aos modelos da indústria 4.0. Congresso Brasileiro de Inovação e Gestão de Desenvolvimento do Produto. Recuperado de https://repositorio.unb.br/bitstream/10482/37046/3/EVENTO_ModelosMaturidadeCMM.pdf DOI: https://doi.org/10.5151/cbgdp2019-18
Sjodin, D. R., Parida V., Leksell, M., & Petrovic, A. (2018). Smart Factory Implementation and Process Innovation. Research-Technology Management, 61(5), 22-31. https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2018.1471277 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2018.1471277
The World Bank. (n.d.). Financiamento para Pequenas e Médias Empresas (PME’s). Recuperado de https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/smefinance
Tortorella, G. L., & Fettermann, D. (2018). Implementation of Industry 4.0 and lean production in Brazilian manufacturing companies. International Journal of Production Research, 56(8), 2975-2987. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1391420 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1391420
Zhong R. Y., Xu, X., Klotz, E., & Newman, S. T. (2017). Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering, 3(5), 616-630. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.015
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Brazilian Journal of Production Engineering

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.