Turnover em obras de montagem eletromecânica: aplicação de Machine Learning na gestão de pessoas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47456/bjpe.v11i4.50222Palavras-chave:
Rotatividade, RH, Montagem eletromecânicaResumo
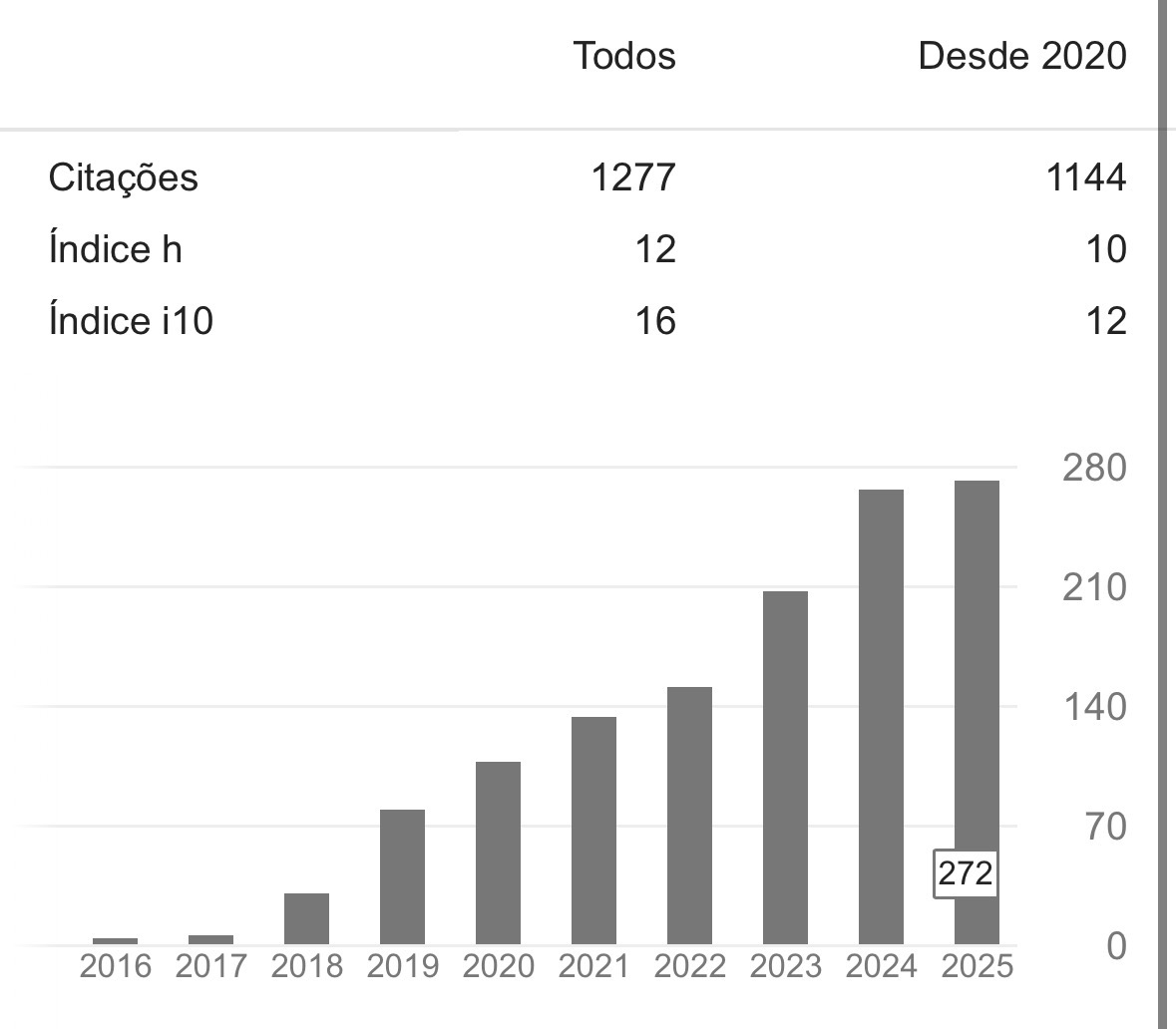
Este estudo investigou os fatores que influenciam a substituição de colaboradores em obras de montagem eletromecânica, com foco na aplicação de técnicas estatísticas e de aprendizado de máquina para apoiar a gestão de pessoas. A pesquisa utilizou uma base de 7.333 registros de desligamentos ocorridos entre janeiro de 2023 e julho de 2025 em uma empresa brasileira do setor, contemplando variáveis individuais, organizacionais e relacionadas à jornada de trabalho. Após o pré-processamento e a análise exploratória dos dados, foram aplicados três modelos de classificação: regressão logística binária (com seleção stepwise), árvore de decisão e Random Forest (com calibração por grid search). Os resultados mostraram que fatores como percentual de abonos, tempo de casa, tipo de obra e estado de residência apresentaram maior relevância para a reposição de vagas. O modelo de Random Forest apresentou o melhor desempenho preditivo, alcançando AUC-ROC de 0,878 e coeficiente de Gini de 0,756, enquanto a regressão logística destacou-se pela interpretabilidade dos coeficientes. Conclui-se que a integração de métodos estatísticos e de machine learning contribui para antecipar cenários de rotatividade, subsidiando estratégias de retenção e alocação mais eficientes na gestão de recursos humanos em projetos industriais.
Downloads
Referências
Aver, G., Miri, D. H., Chais, C., Matte, J., Ganzer, P. P., & Olea, P. M. (2020). Fatores de rotatividade em uma empresa do segmento metalomecânico: Rotativity factors in a mechanical metal segment company. Revista Visão: Gestão Organizacional, 9(2), 168-186. Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning, 45(1), 5-32.
Chiavenato, I. (2014). Gestão de Pessoas: O Novo Papel dos Recursos Humanos nas Organizações. 4 ed. Elsevier Brasil.
Cramér, H. (1999). Mathematical methods of statistics (Vol. 9). Princeton university press.
Dutra, J. S. (2016). Gestão de pessoas: modelo, processos, tendências e perspectivas. 3 ed. Atlas. Elmasri, R., Navathe, S. B., & Pinheiro, M. G. (2005). Sistemas de banco de dados.
Fávero, L. P., & Belfiore, P. (2024). Manual de análise de dados: Estatística e machine learning com Excel®, SPSS®, Stata®, R® e Python®. GEN, LTC.
Hair, J. F. (2009). Multivariate data analysis.
Han, J., Kamber, M., & Pei, J. (2020). Data mining: Concepts and. Techniques, Waltham: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Hastie, T. (2009). The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction.
Hom, P. W., Lee, T. W., Shaw, J. D., & Hausknecht, J. P. (2017). One hundred years of employee turnover theory and research. Journal of applied psychology, 102(3), 530.
Hosmer Jr, D. W., Lemeshow, S., & Sturdivant, R. X. (2013). Applied logistic regression. John Wiley & Sons. James, G. (2013). An introduction to statistical learning with applications in R.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos, A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., & Duchesnay, É. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 12, 2825-2830.
Samuel, F. (2024). Retention Strategies for Project- Based Construction Workers: The Role of Career- Family Balance Initiatives.
Spearman, C. (1961). "General Intelligence" Objectively Determined and Measured.

Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 Passos, G. F. R., & Silva, J. dos S.

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Todos os trabalhos publicados na Brazilian Journal of Production Engineering (BJPE) estão licenciados sob a Creative Commons Atribuição 4.0 Internacional (CC BY 4.0).
Isso significa que:
-
Qualquer pessoa pode copiar, distribuir, exibir, adaptar, remixar e até utilizar comercialmente os conteúdos publicados na revista;
-
Desde que sejam atribuídos os devidos créditos aos autores e à BJPE como fonte original;
-
Não é exigida permissão adicional para reutilização, desde que respeitados os termos da licença.
Esta política está em conformidade com os princípios do acesso aberto, promovendo a ampla disseminação do conhecimento científico.



2.png)